Caffeine is a widely consumed substance that is found in many everyday beverages such as coffee, tea, and energy drinks. While it is known to provide a boost in energy and alertness, it can also lead to addiction and have negative effects on the body. In this article, we will explore the science behind caffeine addiction and its potential health consequences. From the brain to the heart, we will take a closer look at how caffeine affects various systems in the body and what steps can be taken to manage its consumption. So grab a cup of coffee and join us on this journey through the world of caffeine addiction.
The Science Behind Caffeine Addiction and its Effects on the Body
What is Caffeine Addiction?
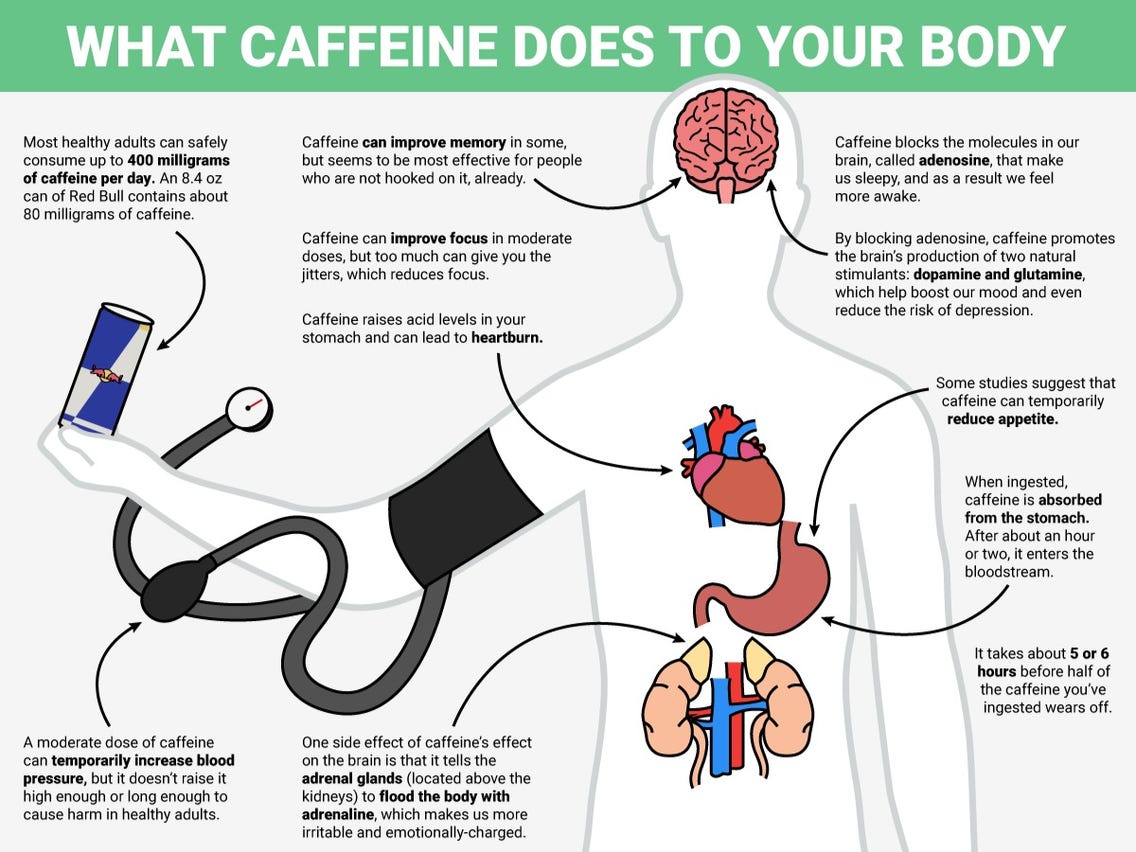
Caffeine is a naturally occurring stimulant found in coffee, tea, and other beverages. It has a chemical structure similar to adenosine, a compound that plays a role in regulating sleep and wakefulness in the body. When caffeine enters the brain, it blocks adenosine receptors, which can lead to increased alertness and reduced fatigue.
However, frequent consumption of caffeine can lead to addiction. This happens when the brain becomes dependent on caffeine to function normally. When caffeine intake is reduced or stopped, withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and irritability can occur.
The Effects of Caffeine on the Body
Caffeine has both positive and negative effects on the body. In small doses, caffeine can improve mental alertness, concentration, and physical performance. It can also temporarily suppress appetite and boost metabolism.
However, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to negative effects on the body. These include increased heart rate, high blood pressure, and anxiety. Caffeine can also interfere with sleep, leading to insomnia and reduced quality of sleep.
Caffeine Addiction and the Brain
Caffeine addiction is a result of changes in the brain’s chemistry. Over time, the brain adapts to regular caffeine intake by increasing the number of adenosine receptors. This leads to a reduced sensitivity to caffeine’s effects and increased tolerance.
When caffeine intake is reduced or stopped, the brain’s adenosine receptors become overstimulated, leading to withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can include headaches, fatigue, and irritability.
How to Reduce Caffeine Intake
Reducing caffeine intake can be challenging, but it is possible. Gradual reduction of caffeine intake over several weeks can help reduce withdrawal symptoms.
Alternatives to caffeine such as herbal teas, decaffeinated coffee, or water can help reduce overall caffeine consumption. Adequate sleep, exercise, and a healthy diet can also help reduce the need for caffeine.
Caffeine Vs Other Stimulants
Caffeine is not the only stimulant available. Other substances such as nicotine, amphetamines, and cocaine can also have stimulant effects. However, these substances are more potent and have greater potential for addiction and negative health effects.
Compared to other stimulants, caffeine is relatively safe and has fewer negative health effects when consumed in moderation.
The Benefits of Caffeine
Despite its potential negative effects, caffeine also has several potential benefits. These include improved mental alertness, concentration, and physical performance. Caffeine can also have positive effects on mood and reduce the risk of some diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and type 2 diabetes.
However, these benefits are only seen in moderate caffeine consumption and can be outweighed by excessive caffeine consumption.
Caffeine and Pregnancy
Pregnant women are advised to limit their caffeine consumption due to potential negative effects on fetal development. High caffeine intake during pregnancy has been linked to low birth weight, preterm birth, and miscarriage.
The recommended daily caffeine intake for pregnant women is less than 200mg per day, or about one cup of coffee.
Caffeine and Children
Caffeine consumption in children should also be limited. Children have a lower tolerance for caffeine and can experience negative effects such as increased heart rate and anxiety.
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children and adolescents avoid caffeine or limit consumption to less than 100mg per day.
Caffeine and Medications
Caffeine can interact with certain medications, including antibiotics, antidepressants, and some pain relievers. These interactions can lead to increased side effects or reduced effectiveness of the medication.
It is important to talk to a healthcare provider before consuming caffeine while taking medications.
Caffeine and Sports Performance
Caffeine is a popular supplement among athletes due to its potential performance-enhancing effects. Caffeine can improve endurance, reduce fatigue, and increase alertness during exercise.
However, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to negative effects such as dehydration and increased heart rate. It is important to consume caffeine in moderation and stay hydrated during exercise.
Conclusion
Caffeine addiction is a result of changes in the brain’s chemistry and can lead to negative health effects. However, moderate caffeine consumption can have potential benefits such as improved mental alertness and reduced risk of some diseases.
Reducing caffeine intake can be challenging, but gradual reduction over several weeks can help reduce withdrawal symptoms. Alternatives to caffeine such as herbal teas and decaffeinated coffee can also help reduce overall caffeine consumption.
It is important to talk to a healthcare provider before consuming caffeine while taking medications or during pregnancy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is caffeine addiction and how does it affect the body?
Caffeine addiction is a condition that occurs when an individual becomes dependent on caffeine to function normally. Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, increasing alertness and reducing fatigue. However, excessive caffeine consumption can have negative effects on the body, including insomnia, anxiety, tremors, and increased heart rate. Over time, caffeine addiction can lead to more serious health problems, such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
In addition to its physical effects, caffeine addiction can also have psychological effects, such as irritability, depression, and difficulty concentrating. Individuals who are addicted to caffeine may experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to quit, including headaches, fatigue, and irritability.
How does caffeine affect the brain?
Caffeine works by blocking the action of a neurotransmitter called adenosine, which is responsible for promoting relaxation and sleep. By blocking adenosine, caffeine increases levels of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which are associated with increased energy and alertness. However, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to overstimulation of the brain, resulting in anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia.
In addition to its effects on neurotransmitters, caffeine also affects the release of hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which are associated with the body’s stress response. This can lead to increased levels of stress and anxiety in some individuals.
What are the long-term effects of caffeine addiction?
Long-term caffeine addiction can have negative effects on the body, including increased risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and osteoporosis. Excessive caffeine consumption can also lead to digestive problems, such as acid reflux and stomach ulcers. In addition, caffeine addiction can have negative effects on mental health, including anxiety, depression, and difficulty concentrating.
Individuals who are addicted to caffeine may also experience withdrawal symptoms when they try to quit, such as headaches, fatigue, and irritability. These symptoms can make it difficult to quit caffeine and can lead to a cycle of addiction and withdrawal.
How much caffeine is too much?
The amount of caffeine that is considered too much varies depending on the individual and their sensitivity to caffeine. However, in general, consuming more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day can lead to negative effects on the body, including increased heart rate, anxiety, and insomnia.
To put this in perspective, a 12-ounce cup of coffee typically contains between 80 and 120 milligrams of caffeine, while a 12-ounce can of soda contains between 30 and 50 milligrams. Energy drinks can contain much higher levels of caffeine, with some brands containing up to 500 milligrams per serving.
How can caffeine addiction be treated?
Caffeine addiction can be treated through a combination of behavioral and pharmacological therapies. Behavioral therapies may include counseling and support groups, while pharmacological therapies may include medications that help to reduce withdrawal symptoms.
Individuals who are attempting to quit caffeine should do so gradually, reducing their caffeine intake over a period of several weeks. This can help to reduce withdrawal symptoms and make it easier to quit caffeine for good.
It is also important for individuals to identify and address the underlying reasons for their caffeine addiction. This may involve making lifestyle changes, such as improving sleep habits and reducing stress, in order to reduce the need for caffeine to function normally.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Caffeine
In conclusion, caffeine addiction is a real and serious issue that affects millions of people worldwide. The science behind this addiction is complex and involves the brain’s reward system and the release of dopamine. It is important to understand the effects of caffeine on the body and to consume it in moderation.
While caffeine can provide a temporary boost in energy and alertness, overconsumption can lead to negative effects such as anxiety, insomnia, and even addiction. It is important to listen to your body and recognize when you may be consuming too much caffeine.
In order to maintain a healthy relationship with caffeine, it is recommended to limit intake and be mindful of the effects it may have on your body. By understanding the science behind caffeine addiction, we can make informed decisions about our consumption habits and prioritize our overall health and well-being.