Caffeine is a popular substance that is consumed by millions of people every day. This stimulant can be found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and even some medications. But have you ever wondered whether caffeine is a stimulant or a depressant?
The answer may surprise you. While caffeine is commonly thought of as a stimulant, its effects on the body can be more complex than that. In this article, we’ll dive deeper into the science behind caffeine and explore whether it truly fits the definition of a stimulant or if it has depressant properties as well.
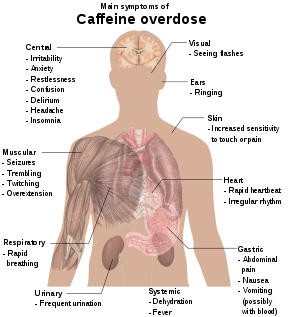
Is Caffeine a Stimulant or Depressant?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant that is found in coffee, tea, and other beverages. It is one of the most widely consumed substances in the world, and its effects on the body have been studied extensively. However, there is still some confusion over whether caffeine is a stimulant or a depressant. In this article, we will explore the science behind caffeine and its effects on the body.
What is Caffeine?
Caffeine is a naturally occurring substance that is found in the leaves, seeds, and fruits of certain plants. It is most commonly consumed in coffee, tea, and soft drinks. Caffeine is classified as a stimulant because it increases activity in the central nervous system. When caffeine is consumed, it blocks the action of a neurotransmitter called adenosine, which is responsible for slowing down brain activity and making us feel tired. This leads to increased alertness, focus, and energy.
Caffeine is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches its peak concentration within 30 to 60 minutes. The effects of caffeine can last for several hours, depending on how much is consumed and individual factors such as metabolism and tolerance.
Stimulant Effects of Caffeine
Caffeine is a powerful stimulant that can have a range of effects on the body. Some of the most common effects of caffeine include increased alertness, energy, and focus. It can also improve mood and reduce feelings of fatigue and drowsiness. In addition, caffeine has been shown to enhance athletic performance, increase metabolism, and suppress appetite.
However, caffeine can also have negative effects on the body when consumed in excess. Some people may experience anxiety, jitteriness, or insomnia when they consume too much caffeine. Caffeine can also cause gastrointestinal distress, such as nausea and diarrhea, particularly in those who are sensitive to its effects.
Depressant Effects of Caffeine
While caffeine is primarily considered a stimulant, it can also have some depressant effects on the body. For example, caffeine can cause a decrease in blood flow to the brain, which can lead to feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness. It can also cause a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, which can be beneficial for those with high blood pressure.
In addition, caffeine has been shown to have a calming effect on the body in some individuals. This may be due to its ability to increase the production of a neurotransmitter called GABA, which is responsible for promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety.
Caffeine vs. Other Stimulants
While caffeine is a powerful stimulant, it is important to note that it is not the only one. There are many other substances that can stimulate the central nervous system, including amphetamines, cocaine, and nicotine. These substances are often more potent than caffeine and can have more intense effects on the body.
However, caffeine is generally considered to be safer than many other stimulants because it is less addictive and has fewer negative side effects. While caffeine can be habit-forming, it is not considered a highly addictive substance like cocaine or amphetamines.
Caffeine Benefits and Risks
Caffeine has been shown to have a number of potential benefits for the body, including improved cognitive function, enhanced athletic performance, and reduced risk of certain diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. However, it is important to remember that caffeine can also have negative effects on the body when consumed in excess.
Some of the risks associated with caffeine consumption include insomnia, anxiety, gastrointestinal distress, and increased heart rate and blood pressure. For this reason, it is recommended that individuals limit their caffeine intake to no more than 400mg per day, which is roughly equivalent to four cups of coffee.
Caffeine and Withdrawal
One of the most well-known effects of caffeine is its ability to cause withdrawal symptoms when consumption is stopped or reduced. This is because caffeine is a habit-forming substance that can lead to physical dependence over time.
Withdrawal symptoms can include headaches, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can be particularly challenging for individuals who consume large amounts of caffeine on a regular basis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, caffeine is a natural stimulant that can have a range of effects on the body. While it is primarily considered a stimulant, it can also have some depressant effects in certain individuals. It is important to consume caffeine in moderation and be aware of the potential risks associated with excessive consumption. By doing so, individuals can enjoy the potential benefits of caffeine while minimizing the negative effects on their health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is caffeine?
Caffeine is a natural stimulant that is commonly found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and some soft drinks. It works by stimulating the central nervous system, which can help to improve alertness and reduce fatigue.
Caffeine is also a diuretic, which means that it can increase urine production and cause dehydration if consumed in large quantities. It is important to consume caffeine in moderation and to stay hydrated throughout the day.
How does caffeine affect the body?
Caffeine affects the body by stimulating the central nervous system, which can increase alertness and reduce fatigue. It can also increase heart rate and blood pressure, which can be beneficial for some people, but can be dangerous for others.
Caffeine can also cause negative side effects, such as headaches, jitters, and insomnia. It is important to be aware of how much caffeine you are consuming and to limit your intake if necessary.
Is caffeine a stimulant or depressant?
Caffeine is a stimulant. It works by stimulating the central nervous system, which can increase alertness and reduce fatigue. However, caffeine can also have negative side effects, such as anxiety and jitters.
Some people may feel that caffeine has a calming effect on them, but this is likely due to the fact that caffeine can improve focus and reduce fatigue, which can make people feel more relaxed.
How much caffeine is too much?
The amount of caffeine that is considered too much varies from person to person. Generally, it is recommended that adults consume no more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day, which is equivalent to about four cups of coffee.
Consuming too much caffeine can lead to negative side effects, such as anxiety, jitters, and insomnia. It is important to be aware of how much caffeine you are consuming and to limit your intake if necessary.
Can caffeine be addictive?
Yes, caffeine can be addictive. Regular caffeine consumption can lead to physical dependence, which means that your body becomes accustomed to the effects of caffeine and you may experience withdrawal symptoms if you stop consuming it.
Withdrawal symptoms can include headaches, fatigue, and irritability. It is important to be aware of your caffeine intake and to gradually reduce your consumption if you decide to cut back on caffeine.
Is caffeine bad for you?
In conclusion, caffeine is a stimulant that can have varying effects on individuals. It is commonly used to increase alertness, focus, and energy, but can also have negative side effects such as anxiety, insomnia, and jitters.
Despite its popularity and widespread use, it is important to recognize that caffeine affects everyone differently. Some people may be more sensitive to its effects, while others may have a higher tolerance. It is also important to monitor your caffeine intake and be aware of the potential risks associated with consuming too much.
Overall, while caffeine can provide a quick boost in energy and alertness, it is important to consume it in moderation and be mindful of its effects on your body. With proper awareness, you can enjoy the benefits of caffeine without experiencing negative consequences.