Have you ever felt jittery, anxious, or had trouble sleeping after consuming too much caffeine? You may have experienced an overdose of this popular stimulant. But how can you tell if you’ve crossed the line from a helpful energy boost to a potentially dangerous overdose? Let’s explore the signs and symptoms of caffeine overdose and how to avoid it.
Caffeine is a widely consumed substance that can be found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and even chocolate. While it can provide a much-needed boost of energy and focus, too much caffeine can lead to negative side effects. So, how much is too much? And what should you do if you suspect you’ve consumed too much caffeine? Let’s dive in and find out.
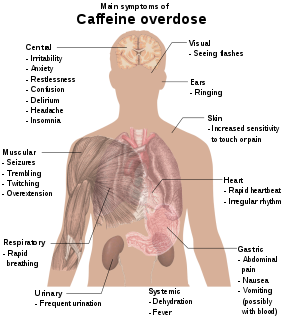
How Do You Know If You’re Overdosing on Caffeine?
Caffeine is a stimulant that is commonly found in coffee, tea, chocolate, and energy drinks. It is known for its ability to increase alertness, improve concentration, and boost energy levels. However, consuming too much caffeine can have negative effects on your body. In this article, we’ll explore the signs and symptoms of caffeine overdose and how to prevent it.
What is Caffeine Overdose?
Caffeine overdose occurs when you consume too much caffeine, typically more than 400mg per day. The amount of caffeine in a drink or food item can vary widely, so it’s important to monitor your intake. Caffeine overdose can cause a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe.
If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it may be a sign of caffeine overdose:
1. Restlessness and Nervousness
Consuming too much caffeine can make you feel jittery, nervous, and restless. You may find it difficult to sit still or concentrate on tasks.
2. Insomnia
Caffeine can interfere with your sleep cycle, making it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep. If you’re consuming caffeine too close to bedtime, it can disrupt your sleep and leave you feeling tired and groggy the next day.
3. Increased Heart Rate and Blood Pressure
Caffeine is a stimulant that can cause your heart rate and blood pressure to increase. If you’re consuming too much caffeine, you may experience heart palpitations or an irregular heartbeat.
4. Headaches
Caffeine can cause headaches, especially if you’re consuming it regularly. If you suddenly stop consuming caffeine, you may experience withdrawal headaches.
5. Nausea and Vomiting
Consuming too much caffeine can irritate your stomach and cause nausea and vomiting. This is more likely to occur if you’re consuming caffeine on an empty stomach.
6. Dehydration
Caffeine is a diuretic, which means it can increase urination and lead to dehydration. If you’re consuming caffeine regularly, it’s important to drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
7. Anxiety and Panic Attacks
Consuming too much caffeine can trigger anxiety and panic attacks, especially if you’re already prone to these conditions.
8. Muscle Tremors
Caffeine can cause muscle tremors and twitching, especially in the hands and fingers.
9. Confusion and Disorientation
If you’re consuming too much caffeine, you may feel confused or disoriented. This is more likely to occur if you’re consuming caffeine in large amounts or if you’re sensitive to its effects.
10. Seizures
In rare cases, caffeine overdose can cause seizures. This is more likely to occur if you’re consuming very large amounts of caffeine or if you have an underlying medical condition.
Contents
How to Prevent Caffeine Overdose
To prevent caffeine overdose, it’s important to monitor your intake and be aware of the caffeine content in the foods and drinks you consume. Here are some tips to help you prevent caffeine overdose:
1. Read Labels
Always read the labels of food and drink items to determine their caffeine content. Be aware that some items, such as energy drinks, may contain very high levels of caffeine.
2. Limit Your Intake
Limit your daily caffeine intake to no more than 400mg per day. This can vary depending on your age, weight, and health conditions, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about what’s right for you.
3. Avoid Caffeine Close to Bedtime
Avoid consuming caffeine close to bedtime, as it can interfere with your sleep cycle and leave you feeling tired the next day.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, especially if you’re consuming caffeine regularly.
5. Know Your Limits
Be aware of your own sensitivity to caffeine and adjust your intake accordingly. If you’re feeling jittery or nervous after consuming caffeine, it may be a sign that you’ve had too much.
Benefits of Caffeine
Despite the risks of caffeine overdose, there are also many benefits to consuming caffeine in moderation. Here are some of the benefits of caffeine:
1. Increased Alertness and Concentration
Caffeine can help you feel more alert and focused, making it a popular choice for students and professionals.
2. Improved Physical Performance
Caffeine can improve physical performance by reducing fatigue and increasing endurance.
3. Weight Loss
Caffeine can help you lose weight by suppressing your appetite and boosting your metabolism.
4. Reduced Risk of Certain Diseases
Caffeine has been linked to a reduced risk of certain diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and liver cancer.
Caffeine vs. Other Stimulants
Caffeine is just one of many stimulants that people use to increase energy and focus. Here are some of the differences between caffeine and other stimulants:
1. Nicotine
Nicotine is a stimulant that is found in tobacco products. Unlike caffeine, nicotine is highly addictive and can have many negative health effects.
2. Amphetamines
Amphetamines are a class of drugs that are used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy. They are much stronger than caffeine and can have many negative side effects.
3. Cocaine
Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant that is illegal in most countries. It is much stronger than caffeine and can have many negative health effects.
Overall, caffeine can be a useful tool for increasing energy and focus, but it’s important to use it in moderation and be aware of its potential risks. By following these tips, you can enjoy the benefits of caffeine without experiencing negative side effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we will answer some common questions related to caffeine overdose.
What is caffeine overdose?
Caffeine overdose occurs when you consume too much caffeine, usually more than 400 milligrams of caffeine in a day. Symptoms of caffeine overdose can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe.
Some common symptoms of caffeine overdose include restlessness, rapid heartbeat, insomnia, dizziness, headaches, and muscle tremors. In severe cases, caffeine overdose can cause seizures, hallucinations, and even death.
How much caffeine is too much?
The amount of caffeine that is considered too much can vary from person to person, depending on factors such as age, weight, and overall health. However, as a general rule, consuming more than 400 milligrams of caffeine in a day can increase the risk of caffeine overdose.
To put this into perspective, 400 milligrams of caffeine is roughly equivalent to four cups of brewed coffee, ten cans of cola, or two energy drinks. It is important to be aware of the caffeine content in the products you consume and to limit your intake accordingly.
What are the long-term effects of caffeine overdose?
Long-term caffeine overdose can lead to a range of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and chronic insomnia. It can also cause anxiety, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible and to take steps to reduce your caffeine intake.
What should I do if I think I am experiencing caffeine overdose?
If you think you are experiencing caffeine overdose, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Symptoms of caffeine overdose can vary from person to person, but may include restlessness, rapid heartbeat, insomnia, dizziness, headaches, and muscle tremors.
In severe cases, caffeine overdose can cause seizures, hallucinations, and even death. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, call emergency services immediately.
How can I reduce my caffeine intake?
If you are concerned about the amount of caffeine you are consuming, there are several steps you can take to reduce your intake. These include switching to decaf coffee or tea, choosing caffeine-free soft drinks, and limiting your intake of energy drinks.
You can also try gradually reducing your caffeine intake over time, rather than quitting cold turkey, to avoid withdrawal symptoms such as headaches and irritability.
Caffeine Overdose: It’s Rare – But It Happens
In conclusion, caffeine is a stimulant that can have both positive and negative effects on the body. While it can boost energy levels and improve mental alertness, consuming too much caffeine can lead to serious health issues. It’s important to be aware of the signs of caffeine overdose, including rapid heartbeat, anxiety, and insomnia.
If you suspect that you may be experiencing caffeine overdose, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately. This can help prevent serious complications and ensure that you receive the appropriate treatment. Additionally, it’s a good idea to monitor your caffeine intake and limit your consumption to a safe and healthy level.
Overall, caffeine is a powerful substance that should be consumed in moderation. By being mindful of your intake and paying attention to your body’s signals, you can enjoy the benefits of caffeine without putting your health at risk. So, be cautious and listen to your body when it comes to caffeine consumption.