Sugar is a ubiquitous ingredient in our diet. It’s found in almost everything we eat and drink, from soda and candy to bread and pasta sauce. But is sugar really as innocent as it seems, or is it more addictive than we realize? Some studies suggest that sugar might be just as addictive as drugs, prompting a growing debate about its effects on our health and wellbeing.
Recent research has shown that sugar activates the same reward centers in the brain as drugs like cocaine and heroin. This has led some experts to argue that sugar addiction should be treated as seriously as drug addiction, with interventions such as counseling and support groups. But is this theory really supported by the evidence, or is it just another example of scaremongering? Let’s take a closer look at the science behind sugar addiction and find out.
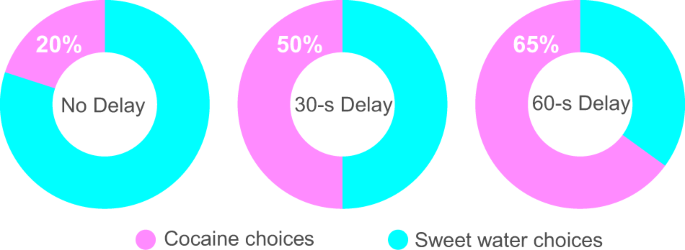
How Addictive Is Sugar Compared to Drugs?
Sugar is a common ingredient in our diet. It is found in almost every food item we consume, from soft drinks to baked goods. Sugar consumption has increased significantly over the years, and for this reason, many people are concerned about the addictive nature of sugar. Some people even argue that sugar is more addictive than drugs.
The Science Behind Sugar Addiction
Sugar addiction is a real phenomenon that has been studied extensively. When we consume sugar, our brain releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is associated with pleasure and reward. This release of dopamine creates a feeling of euphoria. However, the more sugar we consume, the more our brain adapts to it, and we need to consume more sugar to get the same level of pleasure.
Studies have shown that sugar consumption can lead to changes in the brain similar to those that occur with drug addiction. The brain becomes tolerant to sugar, and we need more of it to get the same level of pleasure. Moreover, sugar withdrawal can lead to symptoms similar to drug withdrawal, such as anxiety, depression, and irritability.
The Addictive Nature of Sugar
Sugar is highly addictive, and many people find it difficult to cut down on their intake. The reason for this is that sugar activates the reward centers in our brain, leading to a cycle of craving and consumption. Moreover, sugar is often found in foods that are high in fat and calories, making it easy to overconsume.
The addictive nature of sugar is also linked to its effect on our blood sugar levels. When we consume sugar, our blood sugar levels spike, leading to a rapid release of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate our blood sugar levels, but it also promotes the storage of fat. This can lead to weight gain and further cravings for sugar.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
Consuming too much sugar can have a negative impact on our health. One of the most significant effects of sugar consumption is weight gain. Sugary foods are often high in calories and can lead to overconsumption, which can cause weight gain and obesity.
Moreover, consuming too much sugar can lead to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. This is because sugar consumption can lead to insulin resistance, which can cause high blood sugar levels and eventually lead to diabetes.
Finally, consuming too much sugar can lead to an increased risk of developing heart disease. This is because sugar consumption can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and inflammation, all of which are risk factors for heart disease.
The Benefits of Cutting Down on Sugar
Cutting down on sugar consumption can have many benefits for our health. For example, it can lead to weight loss and a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Moreover, cutting down on sugar can lead to better dental health, as sugar is a major contributor to tooth decay.
Cutting down on sugar can also have a positive impact on our mood and energy levels. Sugar consumption can lead to an energy crash and mood swings, which can be avoided by cutting down on sugar intake.
Sugar vs. Drugs
Comparing sugar to drugs is a controversial topic, but there are some similarities between the two. Both sugar and drugs activate the reward centers in our brain, leading to feelings of pleasure and euphoria. Moreover, both sugar and drugs can lead to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms.
However, there are also some key differences between sugar and drugs. Drugs are often illegal and can have severe side effects, while sugar is legal and widely available. Moreover, while sugar can be addictive, it is not as addictive as drugs such as cocaine or heroin.
How to Cut Down on Sugar
Cutting down on sugar can be challenging, but there are some simple steps you can take to reduce your intake. First, try to avoid sugary drinks such as soda and juice. Instead, opt for water or unsweetened beverages.
Second, try to reduce your consumption of sugary snacks such as candy and cookies. Instead, opt for healthier snacks such as fruit or nuts.
Finally, try to read food labels and avoid foods that are high in sugar. This includes foods that are marketed as healthy, such as granola bars and yogurt.
The Bottom Line
Sugar can be addictive, and consuming too much of it can have negative effects on our health. However, it is not as addictive as drugs, and cutting down on sugar consumption can have many benefits for our health. By making simple changes to our diet, we can reduce our sugar intake and improve our overall health and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction is a term used to describe the compulsive craving for sweet food or drinks. It is a behavioral addiction that affects some people who consume large amounts of sugar on a regular basis.
Similar to drug addiction, sugar addiction can cause changes in the brain’s reward system, leading to a dependency on sugar to feel good. This can result in difficulty controlling sugar intake, and in some cases, withdrawal symptoms when sugar is reduced or eliminated from the diet.
How does sugar addiction compare to drug addiction?
Sugar addiction and drug addiction are both behavioral addictions that have similar effects on the brain’s reward system. Both can lead to cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and difficulty controlling use. However, drug addiction can have more severe health consequences and is often associated with illegal activities.
While sugar addiction may not have the same level of social stigma as drug addiction, it can still have negative effects on health and well-being, such as weight gain, diabetes, and other chronic diseases.
What makes sugar addictive?
Sugar is addictive because it stimulates the release of dopamine in the brain’s reward system, which creates feelings of pleasure and satisfaction. Over time, the brain can become desensitized to dopamine, leading to a need for higher amounts of sugar to achieve the same effect.
In addition, sugar can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, followed by a crash, which can lead to fatigue, mood swings, and further cravings for sugar. This cycle can perpetuate sugar addiction and make it difficult to control sugar intake.
Is sugar more addictive than some drugs?
Research has shown that sugar can be as addictive as some drugs, such as cocaine, in terms of the changes it creates in the brain’s reward system and the behaviors it can cause. However, the physical and psychological effects of drug addiction can be more severe and long-lasting.
It is also important to note that the addictiveness of sugar can vary depending on individual factors, such as genetics, environment, and personal history of addiction.
Can sugar addiction be treated?
Yes, sugar addiction can be treated through a variety of methods, including behavioral therapy, cognitive therapy, and medication. Treatment may involve identifying and addressing underlying psychological or emotional issues that contribute to sugar addiction, as well as developing strategies for managing cravings and reducing sugar intake.
In some cases, a gradual reduction in sugar intake may be recommended to avoid withdrawal symptoms and minimize the risk of relapse. It is important to seek professional help from a qualified healthcare provider or addiction specialist for effective treatment of sugar addiction.
Cocaine vs Sugar
In conclusion, the addictive nature of sugar is comparable to that of drugs. Studies have shown that sugar activates the same pleasure centers in the brain as drugs like cocaine and heroin. This can lead to a cycle of dependence and withdrawal symptoms when sugar intake is reduced.
It is important to note that not all sugars are created equal. Natural sugars found in fruits and vegetables are not as addictive as highly processed sugars found in candy and sugary drinks. It is crucial to limit our intake of these processed sugars and opt for healthier alternatives.
In summary, while sugar may not be classified as a drug, its addictive properties should not be overlooked. By making conscious choices about our sugar intake and opting for healthier alternatives, we can break the cycle of addiction and improve our overall health and wellbeing.