Caffeine is a popular stimulant consumed by millions of people worldwide. It is present in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and several other beverages. While caffeine’s effects vary from person to person, some factors can affect how our bodies react to it. One of these factors is weight. In this article, we explore the question, “Does weight affect caffeine tolerance?” and uncover the science behind it.
If you’re someone who can’t function without their daily cup of coffee or energy drink, you might have noticed that your friend who weighs less than you needs less caffeine to get the same effect. This observation raises the question of whether weight plays a role in caffeine tolerance. We’ll dive deeper into the research and explore whether body weight indeed affects caffeine tolerance and how it affects our body’s reaction to caffeine.
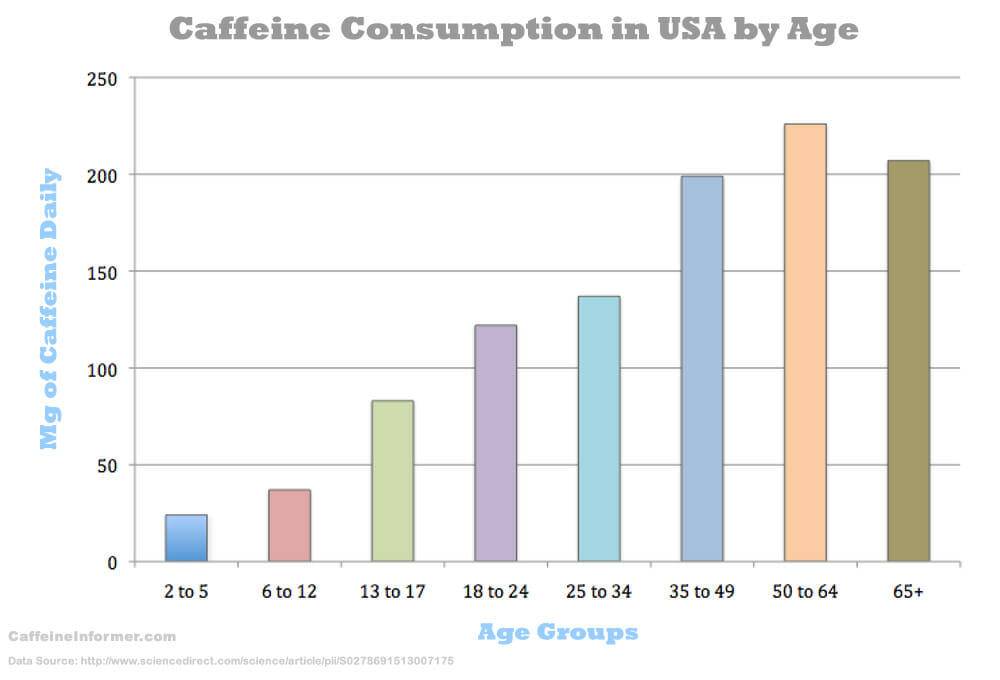
Does Weight Affect Caffeine Tolerance?
Body Weight and Caffeine Metabolism
Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant that is commonly consumed in beverages like coffee, tea, and energy drinks. It is known to have various effects on the body, including increased alertness, improved mood, and enhanced athletic performance. However, the impact of caffeine on an individual’s body can vary depending on various factors, including their body weight.
Research studies have suggested that body weight can influence caffeine metabolism. The metabolism of caffeine is primarily carried out by the liver, where it is broken down into smaller compounds and excreted from the body. Studies have shown that individuals with higher body weight tend to have a slower caffeine metabolism rate in comparison to individuals with lower body weight. This means that heavy individuals may experience the effects of caffeine for a longer time than lighter individuals.
In addition, studies have also suggested that caffeine may have a greater impact on individuals with lower body weight. This is because the same amount of caffeine can have a more significant effect on a smaller body as compared to a larger body. Therefore, individuals with lower body weight may experience stronger effects of caffeine with a much lower dose as compared to individuals with higher body weight.
Factors Affecting Caffeine Tolerance
Caffeine tolerance refers to the body’s ability to tolerate caffeine without experiencing any adverse effects. The level of caffeine tolerance can vary from person to person and can be influenced by various factors. Some of the factors that may affect caffeine tolerance include:
1. Genetics: Studies suggest that genetic factors play a role in determining an individual’s caffeine tolerance level. Certain genetic variations can affect the way caffeine is processed in the body and can influence an individual’s sensitivity to caffeine.
2. Age: As individuals age, their caffeine tolerance level may decrease. This is because older individuals tend to have a slower caffeine metabolism rate, which can lead to the accumulation of caffeine in the body and increase the likelihood of experiencing adverse effects.
3. Gender: Studies have suggested that gender can also play a role in determining an individual’s caffeine tolerance level. Women tend to have a lower caffeine tolerance level than men, which is believed to be due to hormonal differences.
4. Health Conditions: Certain health conditions such as liver disease, anxiety disorders, and heart conditions can affect an individual’s caffeine tolerance level. Individuals with these conditions may be more sensitive to caffeine and may experience adverse effects at lower doses.
Benefits of Caffeine Consumption
Despite the varying effects of caffeine on individuals, it is widely consumed due to its potential benefits. Some of the benefits of caffeine consumption include:
1. Improved Alertness: Caffeine has been shown to improve mental alertness, which can help individuals stay focused and productive.
2. Enhanced Athletic Performance: Caffeine has been shown to improve athletic performance by reducing fatigue and increasing endurance.
3. Reduced Risk of Diseases: Studies have suggested that caffeine consumption may reduce the risk of diseases like Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and liver cancer.
4. Improved Mood: Caffeine consumption has been associated with improved mood and reduced symptoms of depression.
Caffeine vs Other Stimulants
Caffeine is not the only stimulant consumed by individuals. Other stimulants like nicotine and amphetamines are also used for their stimulating effects. However, there are some key differences between these stimulants and caffeine.
Nicotine is a highly addictive stimulant that is commonly consumed through smoking. It has been shown to have various adverse effects on the body, including increased heart rate and blood pressure, and is associated with several health conditions like lung cancer and heart disease.
Amphetamines are a class of drugs that are used to treat conditions like ADHD and narcolepsy. While they can be effective in treating these conditions, they are highly addictive and can have severe adverse effects, including heart problems, mood changes, and addiction.
In contrast, caffeine is a mild stimulant that is widely consumed and has been shown to have potential health benefits. While it can have adverse effects in some individuals, it is generally considered safe for consumption in moderation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, body weight can influence caffeine tolerance levels due to differences in caffeine metabolism rates. While caffeine consumption can have varying effects on individuals, it is generally considered safe for consumption in moderation and is associated with potential health benefits. Factors like genetics, age, gender, and health conditions can also affect caffeine tolerance levels, and individuals should be mindful of their caffeine consumption to avoid adverse effects.
Contents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Is there a connection between body weight and caffeine tolerance?
- Can losing weight increase caffeine sensitivity?
- Does caffeine affect metabolism differently depending on body weight?
- What are some factors that can impact caffeine tolerance besides weight?
- How can individuals manage their caffeine intake based on their personal tolerance?
- The Ugly Truth About Coffee’s Effects On Your Body
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to caffeine tolerance and its possible correlation with weight.
Is there a connection between body weight and caffeine tolerance?
Research suggests that body weight can have an impact on caffeine tolerance. This is because caffeine is a stimulant that affects the central nervous system and metabolism, and both of these systems can be influenced by body weight and composition.
Studies have found that individuals with higher body weights may have a higher tolerance to caffeine, as their bodies may metabolize caffeine more efficiently than those with lower body weights. However, this is not always the case, as genetics, age, and other factors can also play a role in caffeine tolerance.
Can losing weight increase caffeine sensitivity?
While losing weight may lead to a decrease in caffeine tolerance for some individuals, it is not a guaranteed outcome. This is because weight loss can affect the way the body metabolizes caffeine, but it can also impact other factors such as stress levels, sleep patterns, and overall health.
Individuals who are trying to reduce their caffeine intake may find that losing weight can help to support this goal, but it is important to do so in a healthy and sustainable way, as rapid weight loss can have negative impacts on overall health and wellbeing.
Does caffeine affect metabolism differently depending on body weight?
Research has shown that caffeine can affect metabolism differently depending on an individual’s body weight and composition. For example, individuals with higher body weights may experience a greater increase in metabolic rate after consuming caffeine than those with lower body weights.
However, it is important to note that the impact of caffeine on metabolism can vary depending on a variety of factors, including age, gender, genetics, and overall health. Additionally, the effects of caffeine on metabolism may be short-lived and not have a significant impact on overall weight loss or management.
What are some factors that can impact caffeine tolerance besides weight?
While body weight can be a factor in caffeine tolerance, there are many other factors that can impact an individual’s sensitivity to caffeine. These include genetics, age, gender, overall health, and medication use.
Additionally, factors such as stress levels, sleep patterns, and diet can also play a role in an individual’s caffeine tolerance and sensitivity. It is important for individuals to be aware of their own personal responses to caffeine and to make adjustments to their intake as needed to support their overall health and wellbeing.
How can individuals manage their caffeine intake based on their personal tolerance?
Individuals can manage their caffeine intake based on their personal tolerance by paying attention to their own responses to caffeine and making adjustments as needed. This may involve reducing or increasing caffeine intake, experimenting with different sources of caffeine, or adjusting the timing of caffeine consumption.
It is important for individuals to be aware of the potential impacts of caffeine on their sleep, stress levels, and overall health, and to make choices that support their overall wellbeing. Consulting with a healthcare professional can also be helpful in managing caffeine intake and addressing any concerns related to caffeine and health.
The Ugly Truth About Coffee’s Effects On Your Body
In conclusion, it appears that weight does play a role in caffeine tolerance. Research suggests that individuals with a higher body weight may require more caffeine to experience the same effects as those with a lower body weight. However, this is not a hard and fast rule, as genetics, lifestyle, and other factors can also influence caffeine tolerance.
It is important to remember that while caffeine can provide a boost of energy and focus, it is still a drug and should be consumed in moderation. Too much caffeine can lead to negative side effects such as anxiety, jitters, and insomnia.
Ultimately, the best way to determine your own caffeine tolerance is to pay attention to how your body reacts to different amounts of caffeine. If you find yourself experiencing unpleasant side effects, it may be time to cut back on your caffeine intake. As with any substance, listen to your body and make choices that prioritize your health and well-being.