Sugar is a common ingredient in many of our favorite foods and drinks. From cakes and candies to soft drinks and juices, it seems like we just can’t get enough of it. But have you ever wondered why we crave sugar so much? Some people believe that sugar increases dopamine in the brain, which can give us feelings of pleasure and reward. But is this really true?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in our brain’s reward system. It’s responsible for feelings of pleasure, satisfaction, and motivation. Many studies have shown that certain activities, such as exercise and listening to music, can increase dopamine levels. But what about sugar? In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the link between sugar and dopamine to determine whether or not sugar really does increase dopamine in the brain.
Does Sugar Increase Dopamine?
What is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a chemical messenger in the brain that is responsible for transmitting signals between neurons. It plays a crucial role in behavior, motivation, and reward. Dopamine is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it is associated with feelings of pleasure and happiness.
Many activities that we find enjoyable, such as eating, sex, and exercise, all stimulate the release of dopamine in the brain. This is why dopamine is often linked to addiction and why some people may feel a “rush” or “high” after engaging in certain activities.
What is Sugar?
Sugar is a type of carbohydrate that is found naturally in many foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. It is also added to many processed foods and beverages, such as soda, candy, and baked goods. Sugar is often used to enhance the taste of foods and make them more appealing.
There are many different types of sugar, including glucose, fructose, and sucrose. These sugars all have different effects on the body and brain, and some may be more harmful than others.
How Does Sugar Affect Dopamine?
Research has shown that consuming sugar can increase the release of dopamine in the brain. This is because sugar stimulates the same reward centers in the brain as other pleasurable activities, such as sex and drugs.
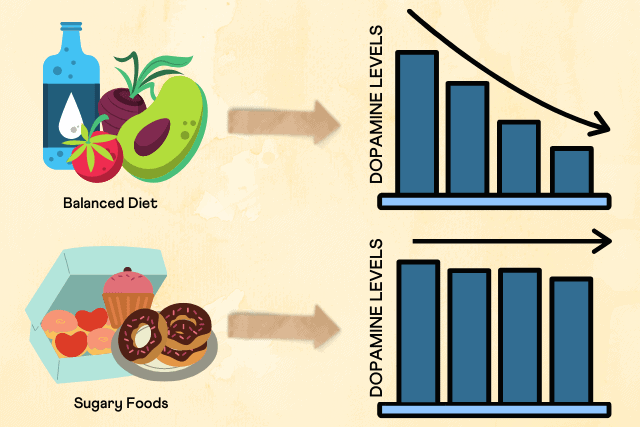
However, the effect of sugar on dopamine release may vary depending on the individual and the type of sugar consumed. Some studies have found that consuming high levels of fructose, a type of sugar found in many processed foods, may lead to a decrease in dopamine receptors in the brain over time, which could contribute to addiction and other health issues.
Sugar vs Other Rewards
Although sugar can stimulate the release of dopamine in the brain, it is important to note that this effect is not unique to sugar. Many other pleasurable activities, such as exercise, sex, and socializing, can also stimulate the release of dopamine. In fact, some studies have suggested that these activities may be more effective at increasing dopamine levels than sugar or other drugs of abuse.
Furthermore, consuming too much sugar can have negative effects on health, such as weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease.
Benefits of Limiting Sugar Intake
Limiting sugar intake can have many benefits for overall health and well-being. Some potential benefits of reducing sugar consumption include:
- Improved weight management
- Better blood sugar control
- Lower risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease
- Improved energy levels
- Better dental health
Conclusion
While consuming sugar can increase the release of dopamine in the brain, this effect is not unique to sugar and may vary depending on the individual and the type of sugar consumed. It is important to remember that consuming too much sugar can have negative effects on health and well-being. Limiting sugar intake and focusing on other pleasurable activities, such as exercise and socializing, may be more effective at increasing dopamine levels and promoting overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions regarding the relationship between sugar and dopamine.
What is dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter in the brain that is associated with pleasure, reward, and motivation. It plays a key role in regulating movement, mood, and cognitive function. Dopamine is released in response to various stimuli, including food, sex, and drugs.
While dopamine is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, it is more accurate to say that it is involved in the experience of pleasure and reward. Dopamine does not cause pleasure directly, but rather motivates us to seek out pleasurable experiences.
How does sugar affect dopamine levels?
Sugar can increase dopamine levels in the brain. When we consume sugar, it triggers the release of dopamine in the reward center of the brain, which reinforces the behavior of eating sweets. Over time, this can lead to a cycle of cravings and addiction.
It’s worth noting that other factors can also affect dopamine levels, such as stress, exercise, and social interaction. So while sugar may play a role in dopamine regulation, it is not the only factor at play.
Is sugar addiction real?
While there is some debate among experts, many believe that sugar addiction is a real phenomenon. When we eat sugar, it can trigger a release of dopamine in the brain that reinforces the behavior of seeking out more sugar. Over time, this can lead to cravings and a dependence on sugar.
Some research has also shown that sugar can have effects on the brain similar to those of drugs of abuse, such as increased tolerance and withdrawal symptoms. However, more research is needed to fully understand the nature of sugar addiction.
Can reducing sugar intake help with dopamine regulation?
Reducing sugar intake may be beneficial for dopamine regulation, as it can help to break the cycle of sugar cravings and addiction. When we consume less sugar, our brains may become less reliant on dopamine as a reward mechanism, which can help to restore natural dopamine regulation.
It’s important to note, however, that reducing sugar intake alone may not be enough to address dopamine regulation issues. Other lifestyle factors, such as stress management and exercise, may also play a role.
What are some healthy alternatives to sugar?
There are many healthy alternatives to sugar that can be used in cooking and baking. Some popular options include stevia, honey, maple syrup, and coconut sugar. These alternatives are often less processed than white sugar and may have additional health benefits.
It’s worth noting that even natural sweeteners should be consumed in moderation, as they can still trigger a release of dopamine in the brain. It’s important to find a balance that works for you and your individual needs.
How sugar affects the brain – Nicole Avena
In conclusion, the answer to whether sugar increases dopamine levels is not a simple yes or no. While sugar does have the potential to increase dopamine release in the short term, the long-term effects of excessive sugar consumption may actually reduce dopamine levels and lead to addiction-like behaviors.
It is important to note that dopamine is not the only factor in sugar addiction, and other neurotransmitters and psychological factors may also play a role. Additionally, the effects of sugar on dopamine may vary depending on individual genetics and lifestyle factors.
Overall, it is clear that excessive sugar consumption can have negative effects on both physical and mental health. Moderation and balance in our diets are key to maintaining overall well-being and preventing addiction-like behaviors.