Coffee is a staple for many people around the world, with over 400 billion cups of coffee consumed annually. The beverage is known for its ability to help people stay alert and focused. However, there is a growing concern about the potential risks of consuming too much caffeine, including the risk of stroke.
A stroke occurs when there is a disruption in the blood flow to the brain. There are several factors that can increase the risk of stroke, including high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. But can too much caffeine also contribute to the risk of stroke? In this article, we will explore the relationship between caffeine and stroke and uncover what the latest research says about this topic.
Can Too Much Caffeine Cause a Stroke?
If you’re a coffee lover, you may have wondered whether you could be at risk of having a stroke due to your caffeine intake. Caffeine is one of the most commonly consumed stimulants in the world, and while it can provide a temporary boost of energy and alertness, too much of it can have potential health risks. In this article, we’ll explore whether excessive caffeine consumption can lead to a stroke and how you can reduce your risk.
What Is a Stroke?
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. As a result, brain cells begin to die, and the functions controlled by that part of the brain can be affected, such as speech, movement, and memory. Strokes can be caused by a variety of factors, including high blood pressure, smoking, and high cholesterol levels.
Is Caffeine Linked to Strokes?
While caffeine is a stimulant that can temporarily increase blood pressure and heart rate, studies have found mixed results regarding its link to strokes. Some studies suggest that high caffeine intake may increase the risk of stroke, while others show no significant association. However, it’s important to note that most of these studies have been observational and cannot prove that caffeine directly causes strokes.
How Much Caffeine Is Too Much?
The amount of caffeine that can lead to adverse effects varies from person to person and depends on factors such as age, weight, and tolerance. In general, consuming more than 400 milligrams of caffeine per day (equivalent to four cups of coffee) can lead to symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, and rapid heart rate. In extreme cases, caffeine overdose can cause seizures, coma, and even death.
Reducing Your Risk of Stroke
While the link between caffeine and strokes is not fully understood, there are several lifestyle changes you can make to reduce your risk of having a stroke. These include:
- Quitting smoking – smoking doubles the risk of having a stroke
- Eating a healthy diet – a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the risk of stroke
- Exercising regularly – being physically active can lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which are risk factors for strokes
- Maintaining a healthy weight – being overweight or obese increases the risk of having a stroke
- Limiting alcohol consumption – excessive alcohol consumption can increase blood pressure and the risk of stroke
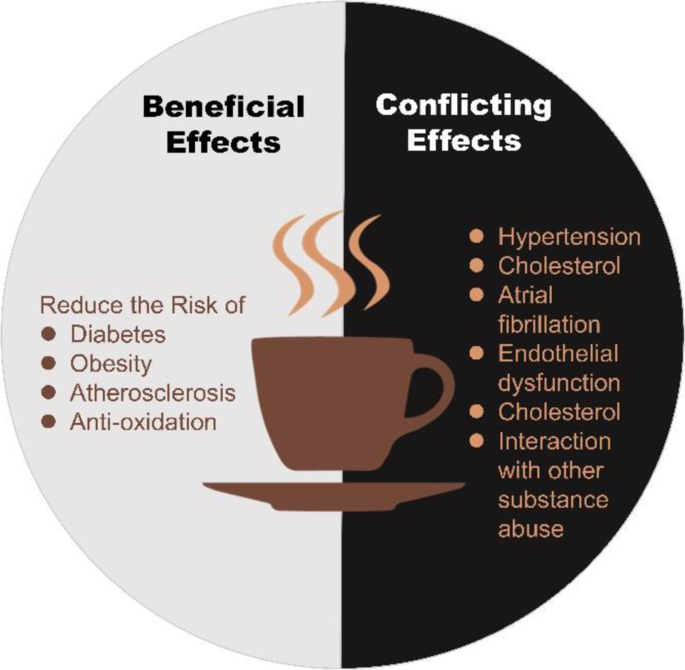
Benefits of Caffeine
While excessive caffeine intake can have potential health risks, moderate caffeine consumption (up to 400 milligrams per day) can have some benefits. These include:
- Increased alertness and concentration
- Improved cognitive function
- Reduced risk of certain diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s
- Enhanced athletic performance
Caffeine vs. Other Drinks
Compared to other drinks, such as sugary sodas and energy drinks, coffee and tea can be a healthier choice due to their lower sugar and calorie content. However, it’s important to consume them in moderation and choose low-fat milk and natural sweeteners instead of cream and sugar. Additionally, it’s important to note that decaffeinated coffee and tea can still provide health benefits without the potential risks of excessive caffeine intake.
Conclusion
While the link between caffeine and strokes is not fully understood, consuming excessive amounts of caffeine can have potential health risks. To reduce your risk of having a stroke, it’s important to make healthy lifestyle choices and consume caffeine in moderation. By following these tips, you can enjoy the benefits of caffeine without putting your health at risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about the relationship between caffeine and stroke:
How much caffeine is safe to consume?
According to the American Heart Association, moderate caffeine consumption, which is defined as 300 milligrams of caffeine per day or less, is generally safe for most people. This is equivalent to about three cups of coffee. However, individual tolerance to caffeine can vary, and some people may be more sensitive to its effects than others. It’s important to be aware of how much caffeine you’re consuming and to monitor your own reactions to it.
Consuming more than 500-600 milligrams of caffeine per day can lead to negative effects such as anxiety, insomnia, and rapid heartbeat. It’s also important to note that certain health conditions, such as high blood pressure, may increase sensitivity to caffeine and require even lower consumption levels.
What is the relationship between caffeine and stroke?
Research has shown that excessive caffeine consumption may increase the risk of stroke. Caffeine can cause a temporary increase in blood pressure and heart rate, which can put extra strain on the cardiovascular system. Over time, this can contribute to the development of conditions such as hypertension and atherosclerosis, which are risk factors for stroke.
However, it’s important to note that the relationship between caffeine and stroke is complex and can vary depending on individual factors such as age, overall health, and lifestyle. More research is needed to fully understand this relationship.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
The symptoms of a stroke can vary depending on the location and severity of the brain damage. Common symptoms include sudden weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or understanding speech, vision problems, severe headache, and dizziness or loss of coordination. It’s important to seek medical attention immediately if you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, as prompt treatment can help reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Remember the acronym “FAST” to help recognize the signs of stroke: Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, Time to call emergency services.
How can I reduce my risk of stroke?
There are several lifestyle changes that can help reduce your risk of stroke. These include maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and managing chronic health conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes. It’s also important to be aware of your family history of stroke and to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
In addition, you can reduce your risk of stroke by monitoring your caffeine consumption and avoiding excessive intake. Remember to stay within the recommended moderate intake levels of 300 milligrams per day or less.
What should I do if I’m concerned about my caffeine consumption?
If you’re concerned about your caffeine consumption, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you determine a safe level of intake based on your individual health profile and provide guidance on ways to reduce your consumption if necessary. It may also be helpful to track your caffeine intake and monitor how it affects your overall health and wellbeing.
Remember, moderation is key when it comes to caffeine consumption, and staying within the recommended limits can help minimize the risk of negative health effects such as stroke.
Does Coffee Prevent Heart Attacks And Strokes? Journal Club
In conclusion, while caffeine consumption has been linked to an increased risk of stroke, the evidence is not conclusive. It is important to note that moderation is key, and excessive caffeine intake should be avoided. Additionally, it is crucial to manage other risk factors for stroke such as high blood pressure, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle. Consulting a healthcare professional regarding caffeine consumption and overall stroke prevention strategies is recommended. Overall, awareness and moderation are essential in maintaining good health and reducing the risk of stroke.