Caffeine is a widely consumed substance that is found in many food and beverage products. It is known for its ability to boost energy, improve mental alertness, and even suppress appetite. However, recent studies have suggested that caffeine withdrawal may have the opposite effect, causing a loss of appetite in some individuals.
If you are someone who relies on caffeine to get through your day or to help you manage your weight, you may be interested to learn more about the potential side effects of caffeine withdrawal. In this article, we will explore the question of whether caffeine withdrawal can cause a loss of appetite, and what you can do to manage any symptoms you may experience.
Can Caffeine Withdrawal Cause Loss of Appetite?
Caffeine is one of the most consumed stimulants around the world. It is present in various products, such as coffee, tea, chocolate, energy drinks, and some medications. Most people consume caffeine to boost their energy levels and increase their alertness. However, caffeine consumption can lead to addiction, and when people try to quit caffeine, they can suffer from withdrawal symptoms. One of the most common caffeine withdrawal symptoms is loss of appetite. In this article, we’ll explore whether caffeine withdrawal can cause loss of appetite and what can be done to alleviate this symptom.
What is Caffeine Withdrawal?
Caffeine is a stimulant that affects the central nervous system. When people consume caffeine, it blocks adenosine receptors, which are responsible for regulating sleep and wakefulness. This leads to increased alertness and energy levels. However, with regular caffeine consumption, the brain adapts to the presence of caffeine and increases the number of adenosine receptors to maintain balance.
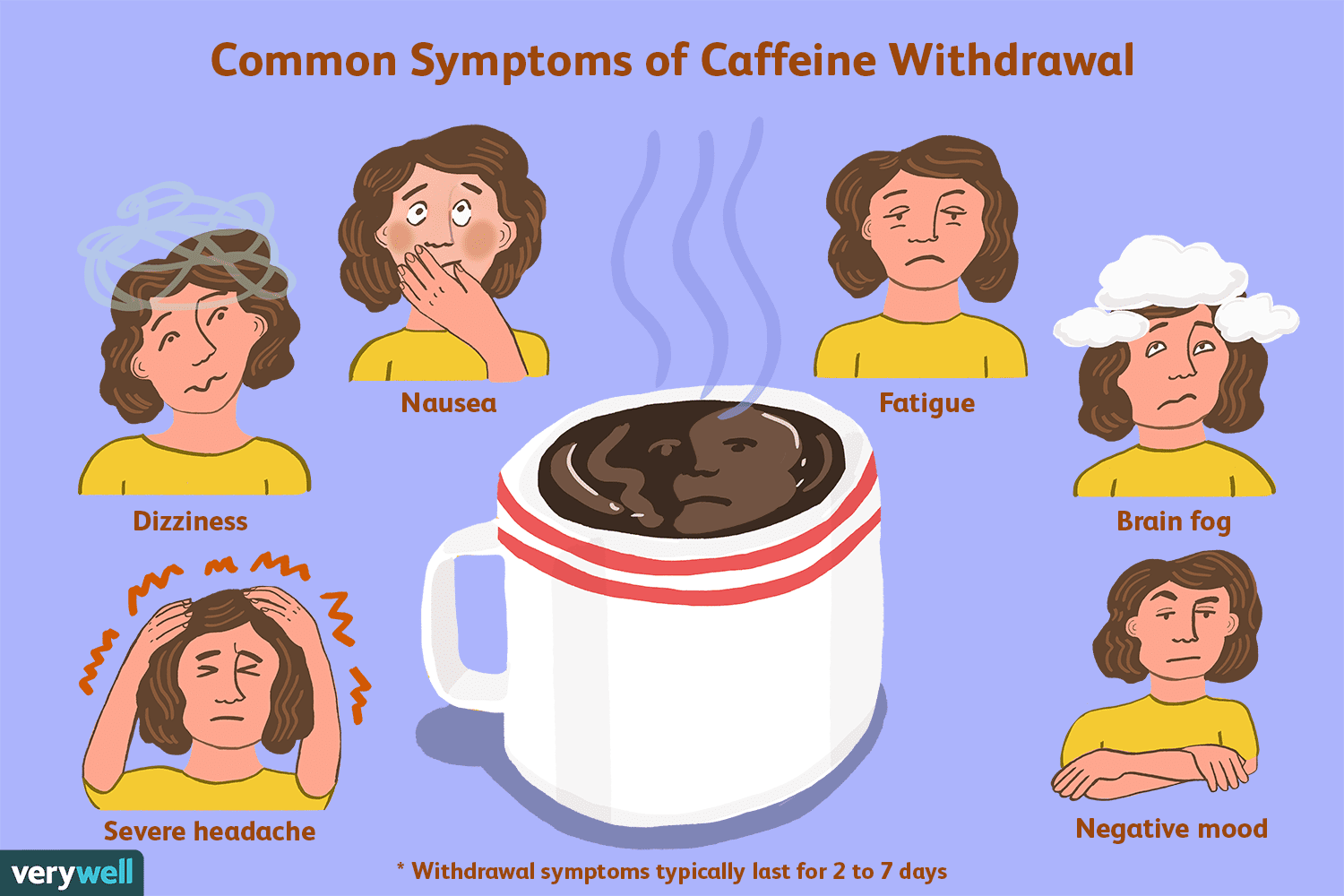
When people abruptly stop consuming caffeine, the brain still has an excess of adenosine receptors, which leads to a sudden drop in energy levels and other withdrawal symptoms. Caffeine withdrawal symptoms can include headache, fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and loss of appetite.
How Does Caffeine Withdrawal Cause Loss of Appetite?
Caffeine affects the appetite by suppressing hunger and increasing satiety. When people consume caffeine, it stimulates the release of adrenaline, which can reduce appetite and increase metabolism. Additionally, caffeine can increase the levels of the hormone cortisol, which can also suppress appetite.
When people quit caffeine, the sudden drop in adrenaline and cortisol levels can lead to an increase in appetite. However, the body still has an excess of adenosine receptors, which can lead to a feeling of fatigue and lethargy, making people less motivated to eat.
Alleviating Loss of Appetite During Caffeine Withdrawal
If you’re experiencing loss of appetite during caffeine withdrawal, there are a few things you can do to alleviate this symptom. Firstly, it’s essential to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water and other fluids. Dehydration can exacerbate withdrawal symptoms, including loss of appetite.
Secondly, try to eat small, frequent meals throughout the day instead of three large meals. This can help to keep your energy levels stable and make it easier to eat when you don’t feel hungry.
Finally, try to incorporate nutrient-dense foods into your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein. These foods can provide your body with the nutrients it needs to function correctly and can help to boost your energy levels.
Benefits of Quitting Caffeine
While caffeine withdrawal can be challenging, there are many benefits to quitting caffeine. Firstly, quitting caffeine can improve sleep quality, as caffeine can interfere with sleep patterns. Secondly, quitting caffeine can reduce anxiety and jitteriness, as caffeine can increase the levels of stress hormones in the body. Finally, quitting caffeine can improve overall health, as excessive caffeine consumption has been linked to various health problems, such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and osteoporosis.
Caffeine Withdrawal vs. Caffeine Intoxication
It’s essential to differentiate between caffeine withdrawal and caffeine intoxication. Caffeine intoxication can occur when people consume too much caffeine, leading to symptoms such as restlessness, palpitations, and nausea. However, caffeine withdrawal occurs when people quit caffeine after regular consumption, leading to symptoms such as headache, fatigue, irritability, and loss of appetite.
Conclusion
In conclusion, caffeine withdrawal can cause loss of appetite due to a sudden drop in adrenaline and cortisol levels, as well as a feeling of lethargy and fatigue. If you’re experiencing loss of appetite during caffeine withdrawal, it’s essential to stay hydrated, eat small, frequent meals, and incorporate nutrient-dense foods into your diet. While quitting caffeine can be challenging, there are many benefits to doing so, including improved sleep quality, reduced anxiety, and improved overall health.
Contents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- How does caffeine affect appetite?
- What are the symptoms of caffeine withdrawal?
- Can caffeine withdrawal cause loss of appetite?
- How long does it take for caffeine withdrawal symptoms to go away?
- What are some strategies for managing caffeine withdrawal symptoms?
- Examining the neurobiology of caffeine withdrawal
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about caffeine withdrawal and its effects on appetite.
How does caffeine affect appetite?
Caffeine is a stimulant that can suppress appetite in some people. It works by increasing the levels of certain hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, which can decrease feelings of hunger and increase feelings of fullness. However, this effect can vary from person to person and may not be significant enough to cause noticeable changes in appetite.
When caffeine is consumed regularly, the body can become accustomed to its effects and may rely on it to regulate appetite. This can lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as increased hunger and cravings, when caffeine is abruptly stopped.
What are the symptoms of caffeine withdrawal?
Caffeine withdrawal can cause a range of symptoms, including headache, fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and decreased motivation. Some people may also experience changes in appetite, such as increased hunger or decreased appetite. These symptoms can last for several days to a week or more, depending on the individual and their caffeine consumption habits.
If you are experiencing symptoms of caffeine withdrawal, it is important to gradually reduce your caffeine intake rather than stopping abruptly, as this can exacerbate symptoms.
Can caffeine withdrawal cause loss of appetite?
Yes, caffeine withdrawal can cause loss of appetite in some people. This is because caffeine can suppress appetite, and when it is suddenly removed from the diet, the body may experience a rebound effect that leads to increased hunger or decreased appetite. However, not everyone will experience this symptom, and it may depend on factors such as the amount of caffeine consumed and the individual’s sensitivity to its effects.
If you are experiencing loss of appetite or other symptoms of caffeine withdrawal, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
How long does it take for caffeine withdrawal symptoms to go away?
The duration of caffeine withdrawal symptoms can vary depending on the individual and their caffeine consumption habits. In general, symptoms can begin within 12 to 24 hours of stopping caffeine and can last for several days to a week or more. However, some people may experience symptoms for longer periods of time, particularly if they were consuming large amounts of caffeine on a regular basis.
To help alleviate symptoms, it is important to stay hydrated, get plenty of rest, and gradually reduce caffeine intake rather than stopping abruptly.
What are some strategies for managing caffeine withdrawal symptoms?
There are several strategies that can help manage caffeine withdrawal symptoms, including gradually reducing caffeine intake rather than stopping abruptly, staying hydrated, getting plenty of rest, and engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga or meditation. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can also help alleviate headaches or other discomfort associated with caffeine withdrawal.
If symptoms persist or are severe, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Examining the neurobiology of caffeine withdrawal
In conclusion, caffeine withdrawal can indeed lead to a loss of appetite. This is because caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, which in turn affects the appetite and digestive system. When caffeine intake is suddenly stopped, the body may experience symptoms such as headaches, fatigue, and a loss of appetite.
However, it’s important to note that not everyone will experience these symptoms to the same degree. Some individuals may not notice any changes in their appetite, while others may experience more severe symptoms. It’s also worth noting that this loss of appetite is usually temporary and should resolve within a few days to a week.
If you are experiencing a loss of appetite due to caffeine withdrawal, there are several things you can do to help alleviate your symptoms. Drinking plenty of water, getting enough rest, and eating small, frequent meals throughout the day can all help to keep your energy levels up and reduce any feelings of nausea or discomfort. With time, your body will adjust to the absence of caffeine and your appetite should return to normal.