Caffeine is a popular stimulant that is consumed by millions of people worldwide. It is commonly found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate. While caffeine is known for its ability to boost energy levels and improve mental clarity, it has also been linked to several health concerns, including high blood pressure. In this article, we will explore the relationship between caffeine withdrawal and high blood pressure and discuss the potential risks associated with consuming too much caffeine.
If you are a regular caffeine consumer, you may have experienced the unpleasant symptoms of caffeine withdrawal, including headaches, fatigue, and irritability. However, recent studies suggest that caffeine withdrawal may also contribute to high blood pressure. This raises concerns about the long-term effects of caffeine consumption and the importance of monitoring our caffeine intake. Read on to learn more about the potential risks of caffeine withdrawal and how to manage your caffeine consumption to maintain healthy blood pressure levels.
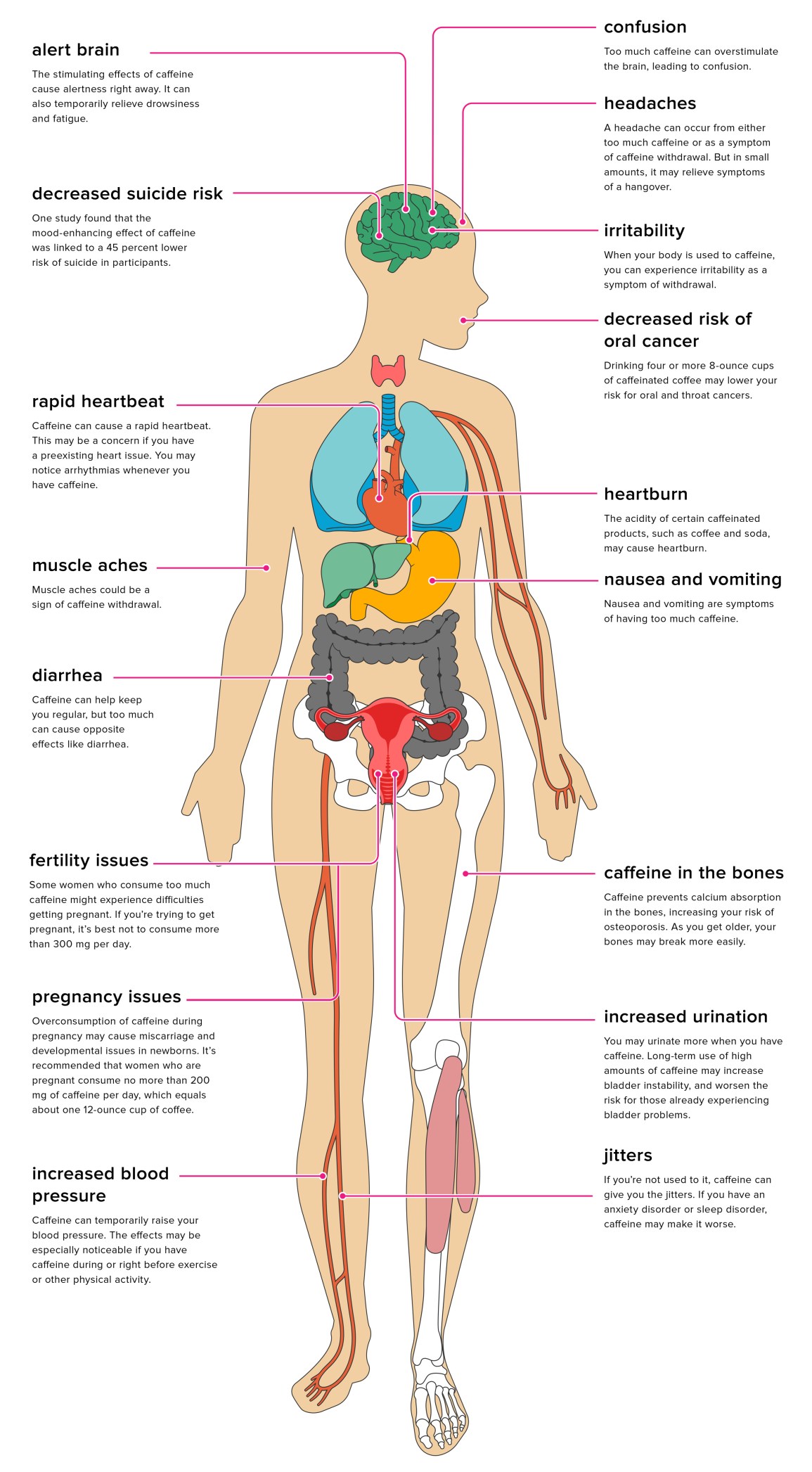
Can Caffeine Withdrawal Cause High Blood Pressure?
Caffeine is a widely consumed stimulant that is found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and various other beverages. While moderate caffeine intake is generally considered safe, excessive consumption can have adverse effects on health, including high blood pressure. However, what happens when you suddenly stop consuming caffeine? Can caffeine withdrawal cause high blood pressure? Let’s explore this topic further.
What is Caffeine Withdrawal?
Caffeine withdrawal is a condition that occurs when regular coffee drinkers abruptly stop or reduce their caffeine intake. Symptoms of caffeine withdrawal can include headaches, fatigue, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and depressed mood. In some cases, caffeine withdrawal can also cause physical symptoms such as nausea and muscle pain.
Caffeine Withdrawal and Blood Pressure
While caffeine withdrawal is not inherently dangerous, it can cause changes in blood pressure that may be concerning for some individuals. Caffeine is a vasoconstrictor, which means that it narrows blood vessels, leading to an increase in blood pressure. When caffeine intake is suddenly stopped or reduced, blood vessels may dilate, which can cause a drop in blood pressure. However, this effect is typically temporary and is not likely to cause significant harm in otherwise healthy individuals.
Who is at Risk?
Individuals who regularly consume large amounts of caffeine may be more susceptible to experiencing blood pressure changes during caffeine withdrawal. Additionally, individuals who have preexisting hypertension or cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk for adverse effects. It is important for these individuals to be aware of the potential risks and consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes to their caffeine intake.
How to Manage Caffeine Withdrawal
If you are experiencing symptoms of caffeine withdrawal, there are several strategies that can help manage these symptoms. Gradually reducing your caffeine intake over time can help minimize the severity of withdrawal symptoms. Staying hydrated and getting adequate sleep can also help alleviate symptoms. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help relieve headaches and muscle pain.
The Benefits of Reducing Caffeine Intake
While caffeine withdrawal can be unpleasant, reducing caffeine intake can have several benefits for overall health. Excessive caffeine consumption has been linked to a variety of health problems, including anxiety, insomnia, and high blood pressure. Reducing caffeine intake can also improve sleep quality, reduce anxiety, and decrease the risk of certain health conditions.
Caffeine vs Decaffeinated Coffee
If you are looking to reduce your caffeine intake, switching to decaffeinated coffee may be an effective strategy. Decaffeinated coffee contains only trace amounts of caffeine, making it a viable alternative for coffee drinkers who are sensitive to caffeine. However, it is important to note that decaffeinated coffee may still contain small amounts of caffeine, and some individuals may still experience withdrawal symptoms when switching to decaf.
The Bottom Line
While caffeine withdrawal can cause changes in blood pressure, these effects are typically temporary and are not likely to cause significant harm in otherwise healthy individuals. However, individuals who regularly consume large amounts of caffeine or have preexisting hypertension or cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk for adverse effects. Gradually reducing caffeine intake over time can help manage withdrawal symptoms and may have long-term health benefits. If you have concerns about caffeine withdrawal or its effects on blood pressure, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5445139/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3777290/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3777290/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5445139/
Contents
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is caffeine withdrawal?
- 2. How does caffeine affect blood pressure?
- 3. Can caffeine withdrawal cause high blood pressure?
- 4. How long does it take for caffeine withdrawal symptoms to go away?
- 5. What are some strategies for managing caffeine withdrawal symptoms?
- Does Caffeine cause High Blood Pressure? ☕
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about caffeine withdrawal and its relation to high blood pressure:
1. What is caffeine withdrawal?
Caffeine withdrawal is a condition that occurs when someone who regularly consumes caffeine suddenly stops or reduces their caffeine intake. Symptoms can include headache, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
While caffeine withdrawal can be uncomfortable, it is generally not considered dangerous and symptoms usually resolve within a few days to a week.
2. How does caffeine affect blood pressure?
Caffeine can cause a temporary increase in blood pressure by constricting blood vessels. This effect is usually mild and short-lived in people who regularly consume caffeine. However, in some individuals, caffeine can cause a more significant and prolonged increase in blood pressure.
If you have high blood pressure, it is recommended that you limit or avoid caffeine intake to help control your blood pressure.
3. Can caffeine withdrawal cause high blood pressure?
Caffeine withdrawal is unlikely to cause high blood pressure. While reducing or stopping caffeine intake can cause some changes in blood pressure, these changes are usually mild and temporary. In fact, some studies suggest that caffeine withdrawal may even lower blood pressure in some individuals.
However, if you have high blood pressure, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider before making any significant changes to your caffeine intake or any other aspect of your diet or lifestyle.
4. How long does it take for caffeine withdrawal symptoms to go away?
The duration of caffeine withdrawal symptoms can vary from person to person, but they typically peak within the first 24-48 hours and then gradually improve over the next few days to a week.
Factors that can affect the duration and severity of caffeine withdrawal symptoms include the amount of caffeine previously consumed, the length of time caffeine was regularly consumed, and individual differences in caffeine metabolism.
5. What are some strategies for managing caffeine withdrawal symptoms?
Some strategies for managing caffeine withdrawal symptoms include gradually reducing caffeine intake over a period of days or weeks, staying hydrated, getting regular exercise, and ensuring adequate sleep and nutrition.
Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can also help with headache or other discomfort associated with caffeine withdrawal, but it is important to follow the recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider if you have any underlying medical conditions or take other medications.
Does Caffeine cause High Blood Pressure? ☕
In conclusion, caffeine withdrawal can potentially cause high blood pressure in some individuals. However, this is not a common occurrence and is usually temporary. The best way to avoid experiencing caffeine withdrawal symptoms is to gradually reduce caffeine intake rather than quitting cold turkey. It is also important to note that high blood pressure can have various causes, and it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing any concerning symptoms. So, if you are a coffee lover, don’t worry too much about the occasional caffeine withdrawal symptoms, but do take care of your health by monitoring your blood pressure regularly.