Caffeine is a popular stimulant consumed by millions of people worldwide. From a cup of coffee in the morning to a can of soda in the afternoon, caffeine provides an instant boost of energy and alertness. However, excessive consumption of caffeine can lead to various health problems, including caffeine withdrawal symptoms.
One of the most common caffeine withdrawal symptoms is dizziness. While caffeine withdrawal is not life-threatening, it can cause discomfort and disrupt your daily routine. In this article, we will explore the relationship between caffeine withdrawal and dizziness and provide tips on how to manage these symptoms effectively.
Can Caffeine Withdrawal Cause Dizziness?
Caffeine is a stimulant found in coffee, tea, and many other beverages and foods. It is a widely consumed substance that can help people stay alert and focused. However, when people consume caffeine regularly, their bodies can become dependent on it. This can lead to caffeine withdrawal when they stop consuming it. One of the common symptoms of caffeine withdrawal is dizziness. In this article, we will explore the relationship between caffeine withdrawal and dizziness.
What is Caffeine Withdrawal?
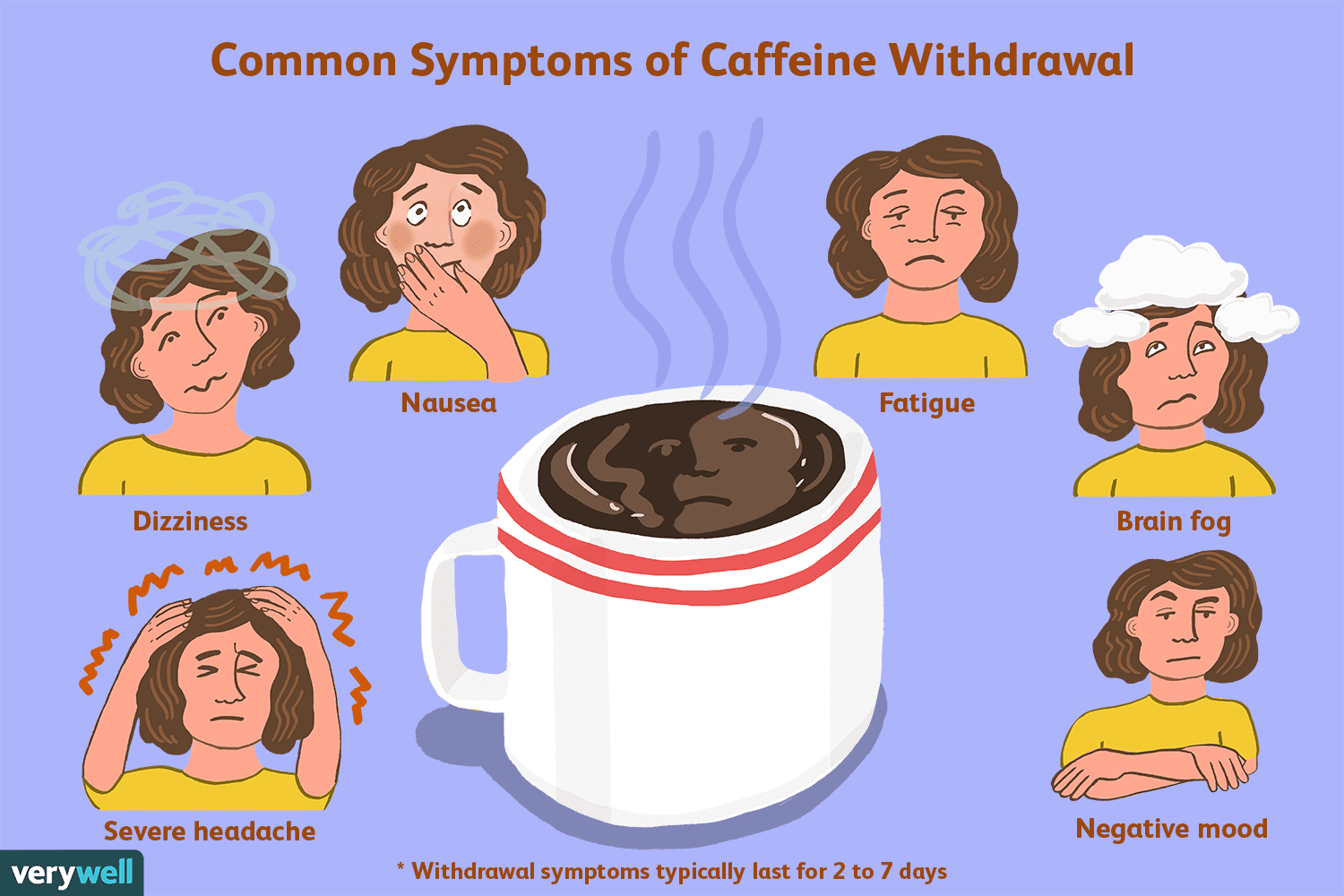
Caffeine withdrawal is a condition that occurs when people who consume caffeine regularly stop consuming it. Caffeine is a psychoactive drug that affects the central nervous system and can cause physical and psychological dependence. When people suddenly stop consuming caffeine, they may experience a range of symptoms, including headache, fatigue, irritability, depression, and dizziness.
What Causes Caffeine Withdrawal?
Caffeine withdrawal occurs because caffeine stimulates the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood and pleasure. When people consume caffeine regularly, their brains adapt to the increased dopamine levels by reducing the number of dopamine receptors. This means that when people stop consuming caffeine, their brains have fewer dopamine receptors to receive the dopamine signals, leading to withdrawal symptoms.
What are the Symptoms of Caffeine Withdrawal?
The symptoms of caffeine withdrawal can vary from person to person but commonly include headache, fatigue, irritability, depression, and dizziness. Dizziness is a feeling of lightheadedness or unsteadiness that can occur when people suddenly stand up or move their heads. It can also be accompanied by nausea, blurred vision, and fainting.
How is Caffeine Withdrawal Treated?
The best way to treat caffeine withdrawal is to gradually reduce caffeine consumption over time to avoid sudden withdrawal symptoms. This can be achieved by reducing the amount of caffeine consumed each day or by gradually switching to decaffeinated beverages. It is also important to stay hydrated and get enough sleep and exercise to help alleviate the symptoms.
How Long Does Caffeine Withdrawal Last?
The duration of caffeine withdrawal can vary from person to person but commonly lasts for a few days to a week. The severity of the symptoms can also vary, with some people experiencing mild symptoms while others may experience more severe symptoms.
How Can Dizziness be Managed During Caffeine Withdrawal?
Dizziness can be managed during caffeine withdrawal by avoiding sudden movements and standing up slowly. It is also important to stay hydrated and maintain a healthy diet to help alleviate the symptoms. If the dizziness persists or is severe, it is important to seek medical attention.
The Benefits of Reducing Caffeine Consumption
Reducing caffeine consumption can have several benefits, including better sleep quality, reduced anxiety, and improved overall health. Caffeine consumption can also lead to dehydration, which can cause headaches and fatigue.
Caffeine vs Decaf
Decaffeinated beverages contain much less caffeine than regular beverages and can be a good alternative for people who want to reduce their caffeine consumption. Decaf still contains a small amount of caffeine, so it is important to check the label to ensure that it is truly decaffeinated.
Conclusion
In conclusion, caffeine withdrawal can cause dizziness, among other symptoms. The best way to manage caffeine withdrawal is to gradually reduce caffeine consumption over time. It is also important to stay hydrated and get enough sleep and exercise to help alleviate the symptoms. Reducing caffeine consumption can have several benefits, including better sleep quality, reduced anxiety, and improved overall health. Decaffeinated beverages can be a good alternative for people who want to reduce their caffeine consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
For those who are regular caffeine consumers, the idea of quitting or reducing their caffeine intake can be quite daunting. One common concern is whether caffeine withdrawal can cause dizziness. Here are some frequently asked questions on the topic:
What is caffeine withdrawal?
Caffeine withdrawal is the process of reducing or eliminating caffeine consumption after regular use. It can cause a range of symptoms, including headaches, fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can occur within a day of reducing caffeine intake and can last for up to a week.
Withdrawal occurs because caffeine is a stimulant that affects the central nervous system. Regular consumption can lead to tolerance, meaning that the body adapts to the presence of caffeine and requires more to achieve the same effects. When caffeine is reduced or eliminated, the body goes through a readjustment period.
Can caffeine withdrawal cause dizziness?
Yes, caffeine withdrawal can cause dizziness, although it is not a common symptom. Dizziness can occur as a result of changes in blood pressure or blood flow to the brain. Caffeine can affect blood pressure by constricting blood vessels, so when caffeine intake is reduced, blood vessels may dilate, leading to a drop in blood pressure and dizziness.
Dizziness can also occur due to dehydration, which can be a side effect of caffeine withdrawal. Caffeine is a diuretic, meaning it increases urine output and can lead to dehydration if not consumed in moderation. When caffeine is reduced, the body may experience a sudden shift in fluid balance, leading to dehydration and dizziness.
What other symptoms can occur during caffeine withdrawal?
In addition to dizziness, caffeine withdrawal can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Difficulty concentrating
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Tremors
- Nausea
These symptoms can vary in severity and duration depending on factors such as caffeine consumption levels, duration of use, and individual differences in metabolism.
How can I manage caffeine withdrawal symptoms?
There are several strategies that can help manage caffeine withdrawal symptoms, including:
- Gradually reducing caffeine consumption instead of quitting cold turkey
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water and other fluids
- Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Getting enough sleep and rest
- Exercising regularly
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation
If symptoms persist or are severe, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
5 Signs and Symptoms of Caffeine Withdrawal
In conclusion, caffeine withdrawal can indeed cause dizziness. It is important to note that this is just one of the many symptoms that can arise from caffeine withdrawal, and it can range in severity depending on the individual.
If you are experiencing dizziness as a result of caffeine withdrawal, it is important to take steps to manage your symptoms. Drinking plenty of water, getting enough rest, and engaging in light exercise can all help to alleviate dizziness and other symptoms.
Ultimately, the best way to avoid caffeine withdrawal symptoms is to gradually reduce your caffeine intake rather than quitting cold turkey. By taking a gradual approach, you can give your body time to adjust to the changes and minimize the risk of experiencing uncomfortable symptoms like dizziness.